
Cloud adoption has become the cornerstone of digital transformation for organizations worldwide. Businesses now rely on the cloud not just for storage and computing, but for agility, innovation, and scalability. However, while the cloud offers immense flexibility, it also introduces a challenge that most organizations struggle with: managing cloud costs without sacrificing performance.
Cloud bills often spiral out of control due to factors like idle resources, poor monitoring, and lack of governance. According to Gartner, organizations waste nearly 30% (Source Cloud Zero) of their cloud spend because of inefficiencies. This makes cloud monitoring and cost optimization not just an operational best practice, but a financial imperative.
This document explores the causes of cloud cost overruns, strategies to optimize spending, best practices for monitoring, and how proactive approaches can save businesses up to 30% in costs—all while ensuring reliability and performance.
1. Understanding Cloud Monitoring
Cloud monitoring is the process of tracking, analyzing, and managing cloud-based resources, services, and applications. It ensures that infrastructure is running optimally, alerts are triggered when issues arise, and performance bottlenecks are identified before they impact end users.
Why It’s Important
- Proactive Problem Detection : Identify and resolve performance issues before they affect business operations.
- Capacity Planning : Monitor usage patterns to predict future resource needs.
- Compliance & Security : Track activities for compliance with regulations and security standards.
- Cost Management : Monitor underutilized resources that can be downsized or decommissioned.
2. Key Metrics in Cloud Monitoring
A robust monitoring strategy focuses on the right metrics. These can vary depending on the application and industry, but generally include:
- CPU Utilization
- Memory Usage
- Disk I/O and Storage Utilization
- Network Latency & Throughput
- Error Rates
- Availability & Uptime
- Cost Metrics
3. The Link Between Monitoring and Cost Optimization
Many organizations treat cloud monitoring and cost optimization as separate functions, but they are deeply connected. Poor visibility into resource usage often leads to waste, while cost optimization without performance insights can cause service degradation.
Example: If a monitoring system detects that 60% of virtual machines (VMs) in a workload are running at below 10% CPU utilization, cost optimization steps can be taken—such as downsizing instance types or consolidating workloads.
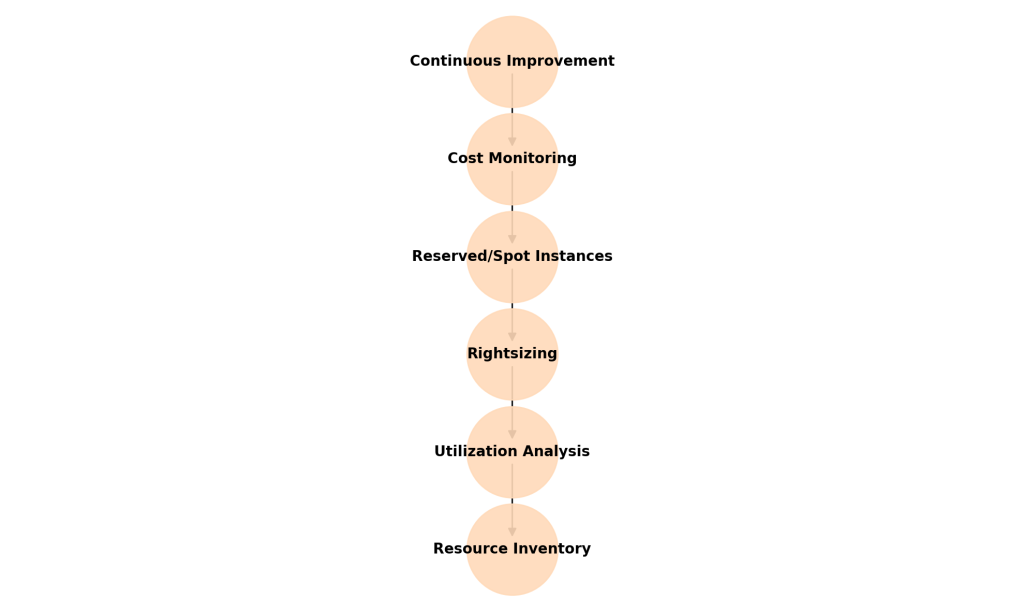
4. Common Causes of Cloud Cost Overruns
- Overprovisioning: Organizations often allocate more CPU, memory, or storage than necessary to ensure ‘performance headroom.’ This leads to inflated bills.
- Idle Resources: Servers often run 24/7 even if needed only during working hours, especially dev/test environments.
- Lack of Auto-Scaling: Without auto-scaling, systems either over-provision (wasting money) or underperform during peaks.
- Data Transfer Costs: Moving data across regions or AZs (availability zone) incurs significant charges, often underestimated.
- Orphaned Resources: Snapshots, unattached volumes, and unused load balancers silently accumulate charges.
5. Strategies for Cloud Cost Optimization
- Rightsizing Resources: Ensure workloads use the right instance size based on actual metrics. AWS/Azure advisors can recommend downscaling.
- Implement Auto-Scaling: Automatically adjust resources to match demand, scaling out during peaks and scaling in during idle times.
- Leverage Reserved and Spot Instances: Reserved Instances save up to 72% on predictable workloads; Spot Instances cut costs for fault-tolerant workloads.
- Turn Off Idle Resources: Shut down non-critical environments after hours. Automation can save 20–30% costs.
- Optimize Storage: Move cold data to cheaper tiers like Glacier or Archive; delete unused snapshots/volumes.
- Monitor and Manage Data Transfer: Reduce cross-region transfers and use CDNs for caching to minimize costs.
6. Best Practices for Cloud Monitoring
- Use a Centralized Monitoring Dashboard : Unify AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, or Datadog.
- Set Threshold-Based Alerts :Trigger alerts for underutilization or cost overruns.
- Enable Log Monitoring : Detect errors, inefficient queries, or unauthorized activity.
- Monitor Cost Metrics Alongside Performance : Couple cost and performance metrics for better decisions.
- Automate Remediation : Auto shutdown idle servers or resize instances.
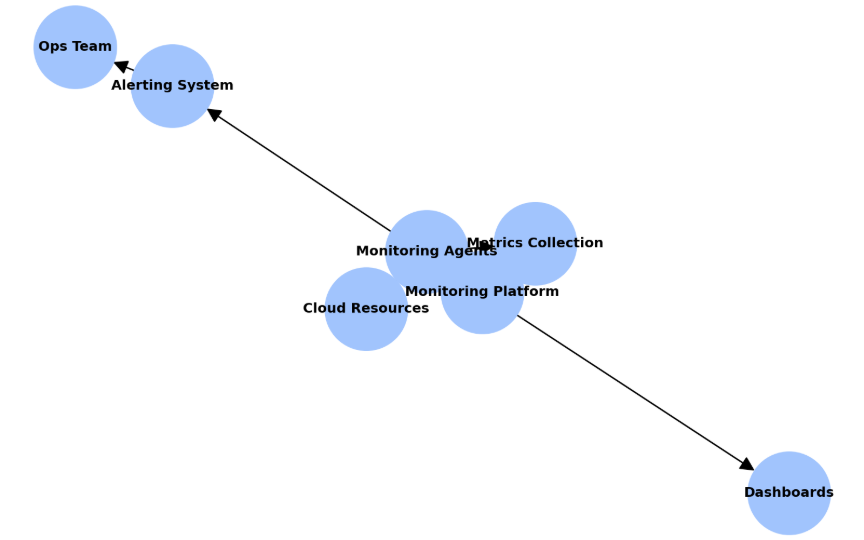
7. Tools for Cloud Monitoring and Cost Optimization
Native Cloud Provider Tools:
- AWS Cost Explorer
- AWS CloudWatch
- Azure Monitor
- Google Cloud Operations Suite
Third-Party Tools:
- Datadog
- New Relic
- Spot.io
- CloudHealth by VMware
8. Building a Culture of Cost-Aware Monitoring
- Reward cost-saving initiatives.
- Include cost dashboards in daily stand-ups.
- Train teams on cloud billing models.
9. The Future of Cloud Monitoring and Cost Optimization
- Predictive Scaling : AI-driven analytics forecast demand and provision resources in advance.
- Automated Cost Governance : Enforce spending limits, tagging, and budgets with automation.
- Sustainability Metrics : Monitor energy efficiency and carbon footprint alongside costs.
Conclusion
Cloud monitoring and cost optimization are essential for sustainable cloud adoption. By identifying cost overruns, applying strategies like rightsizing and auto-scaling, and following monitoring best practices, organizations can save significantly while maintaining reliability. The future lies in predictive, automated, and sustainability-focused monitoring, making optimization smarter and greener.