
Whether you’re just starting out in React or building scalable production-grade apps, handling API calls efficiently is one of the most critical skills. In this blog, I’ll Walk you through how to handle API calls using:
- fetch → for learning and understanding basics
- axios → the best option for beginners and intermediate apps
- React Query → the ultimate tool for production-ready apps
I’ll also provide clear code examples and a final comparison to help you choose what is best for your project
1. fetch – The Native, Low-Level API
The fetch() API comes built into all modern browsers and lets you make HTTP requests using JavaScript. It’s a great way to learn how the web works because it shows you the basic steps of sending and receiving data without hiding too much.
How fetch work behind the scene
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
- The JavaScript engine calls fetch() and hands the task to the browser’s Web APIs.
- The browser builds a Request object with method, headers, body, etc.
- The request passes through the browser’s network stack (DNS, TCP/IP, HTTP).
- A response comes back from the server.
- The browser wraps it in a Response object, and a Promise is returned to your code.
- You manually handle parsing (like calling .json()) and errors.
Example using fetch
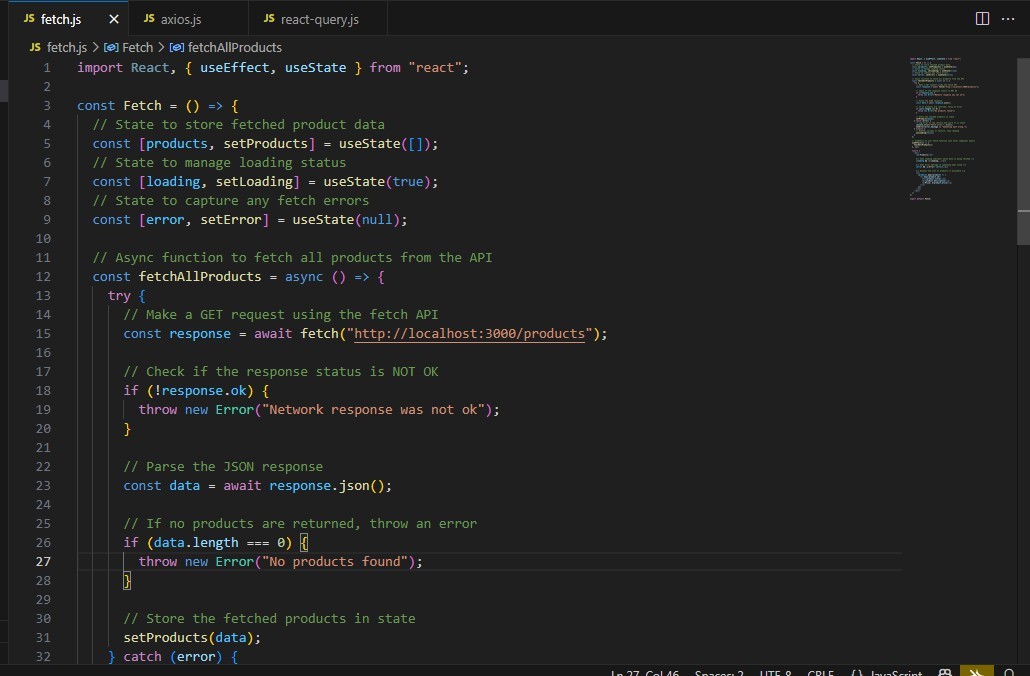
2. axios – Best for Beginners and Intermediate Apps
axios is a promise-based HTTP client with features like interceptors, base URLs, and request cancellation. It’s more beginner-friendly and widely adopted in real-world React apps.
How axios work behind the scene
- When you call axios(), it first creates a config object by merging your settings with defaults (like baseURL, headers, timeout).
- If any request interceptors are defined, they are applied (e.g., for adding tokens).
- Axios then creates an internal XMLHttpRequest (in browsers) or a Node.js HTTP request (in server-side apps).
- The request is sent to the server using the same network stack (DNS → TCP/IP → HTTP).
When a response is received, Axios:
- Automatically parses JSON
- Applies response interceptors
- Returns a structured Promise with data, status, headers, and config.
Example using axios
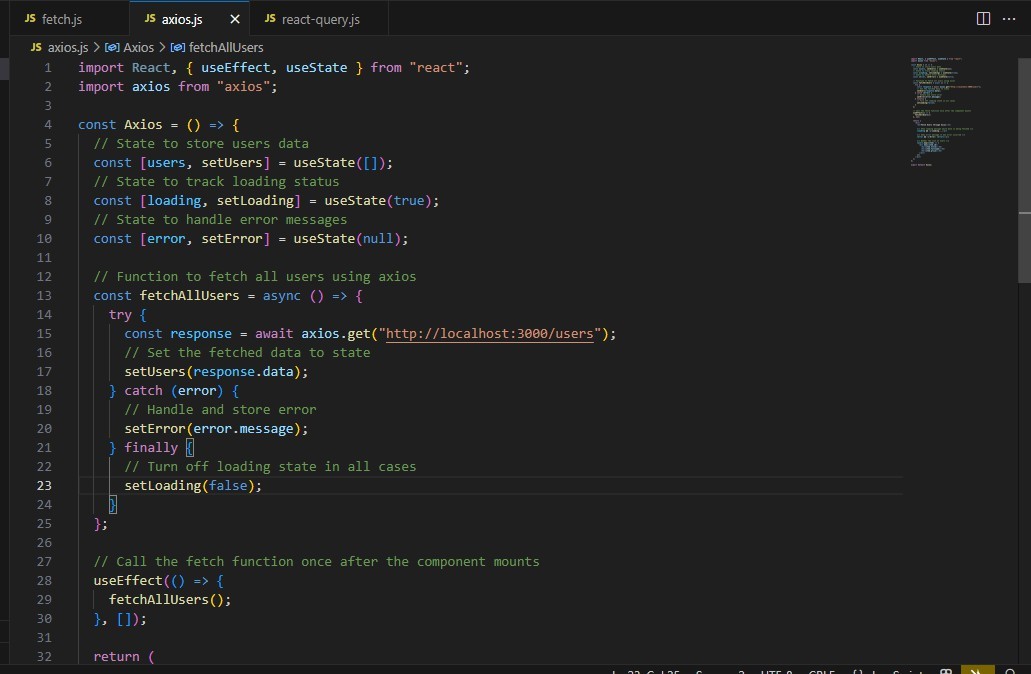
3. React Query – Best for Production Apps
React Query isn’t a replacement for fetch or axios; instead, it manages how, when, and where your API calls happen in React apps. It works on top of fetch/axios and handles caching, background updates, retries, and more.
How React-Query work behind the scene
- You define a query key and a query function (usually using axios or fetch).
- React Query stores this query in an internal cache. If the same query is called again, it returns cached data instantly.
- It tracks the status of every request (loading, success, error) and auto-retries failed requests based on configuration.
- If your component unmounts or the tab loses focus, React Query can pause fetching and automatically refetch when the user returns.
- It handles background sync, pagination, stale data, and deduplication with almost no extra code.
Example using react-query
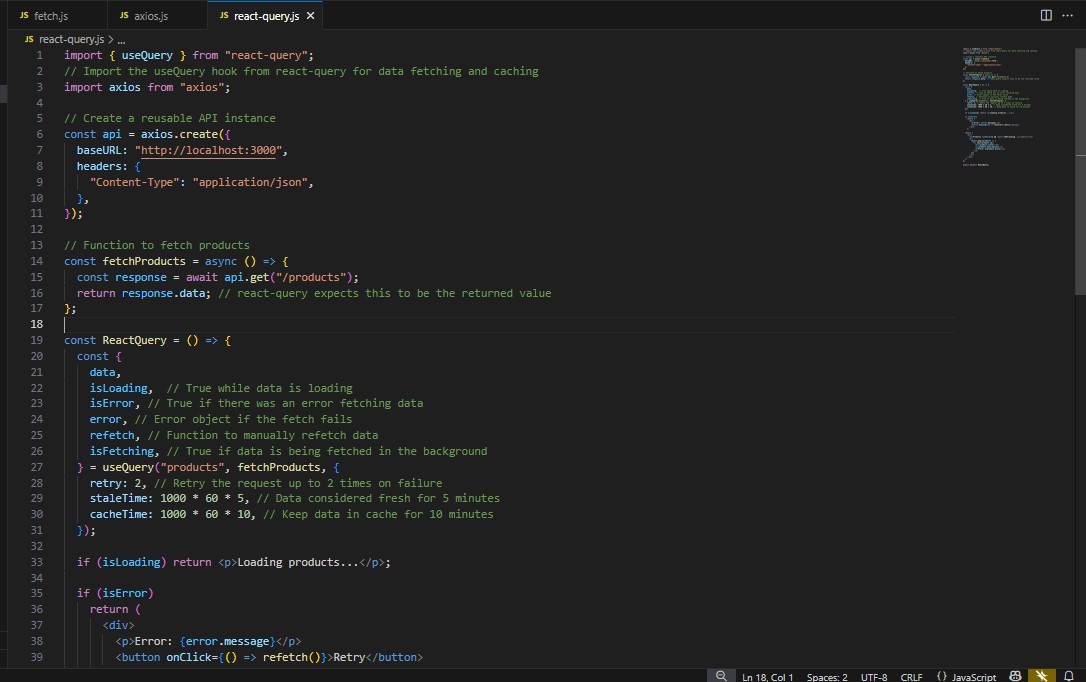
Final Comparison: fetch vs axios vs React Query
| Feature | Fetch (native) | axios (beginner- friendly) | React Query (advanced) |
| Error Handling | Manual try/catch blocks | Built-in error object in response | Automatic error capture + retries + stale states |
| Caching | + No caching by default | + Requires manual implementation | Built-in support for vector pagination, refetch, retry |
| Pagination/Refetch | Manual with useState C useEffect | Manual + extra code | Built-in support for pagination, refetch, retry |
| TypeScript Support | Manual typing + boilerplate | Good with AxiosResponse | Excellent with built- in generics and hooks |
| Interceptors | + Not supported | Can modify requests/responses | Interceptors possible (through axios adapter) |
| Usage Level | Ideal for learners | Suitable for beginners C real apps | Best for large, production-grade applications |
Conclusion
Choosing the right tool for API calls in Reacts is about matching the scope of your project, team experience and future needs:
- Use fetch when you’re learning the basics or building a small app. It’s simple and helps you understand how HTTP works under the hood.
- Use axios for more structure, better error handling, and when you’re working with mid-size apps. It has fantastic community support and simplifies many common tasks.
- Use React Query for large, scalable, production-grade apps. It dramatically reduces boilerplate, manages caching, and improves UX with features like background updates and automatic retries.